Resample¶
- class auglib.transform.Resample(target_rate, *, preserve_level=False, bypass_prob=None, **kwargs)[source]¶
Resample signal to another sampling rate.
Changes number of samples of the audio signal by applying
audresample.resample()to the signal.- Parameters
target_rate (
typing.Union[int,auglib.core.observe.List]) – target rate in Hzpreserve_level (
typing.Union[bool,auglib.core.observe.Base]) – ifTruethe root mean square value of the augmented signal will be the same as before augmentationbypass_prob (
typing.Union[float,auglib.core.observe.Base,None]) – probability to bypass the transformation
Examples
When applying a transform on a file with
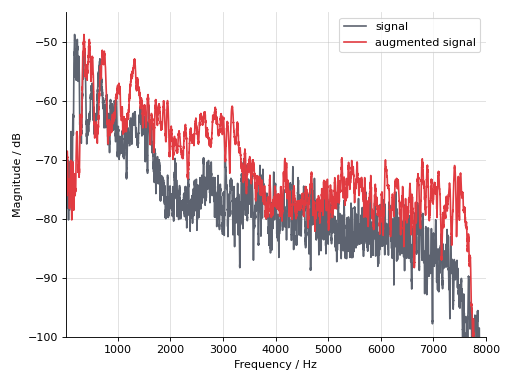
auglib.Augment, it will not change its sampling rate, but its number of samples. Hence, we assume here as well that the sampling rate of the augmented signal stays at 16000 Hz.Resample a speech signal to 8000 Hz, to speed up the signal.
>>> import audb >>> import audiofile >>> import audplot >>> import auglib >>> transform = auglib.transform.Resample(8000) >>> files = audb.load_media("emodb", "wav/03a01Fa.wav", version="1.4.1") >>> signal, sampling_rate = audiofile.read(files[0]) >>> augmented_signal = transform(signal, sampling_rate) >>> audplot.waveform(augmented_signal)

Inspect its magnitude spectrum.
>>> import audmath >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> import seaborn as sns >>> sigs = [signal, augmented_signal] >>> colors = ["#5d6370", "#e13b41"] >>> for sig, color in zip(sigs, colors): ... magnitude, f = plt.mlab.magnitude_spectrum(sig, Fs=sampling_rate) ... # Smooth magnitude ... magnitude = np.convolve(magnitude, np.ones(14) / 14, mode="same") ... plt.plot(f, audmath.db(magnitude), color=color) >>> plt.xlim([10, 8000]) >>> plt.ylim([-100, -45]) >>> plt.ylabel("Magnitude / dB") >>> plt.xlabel("Frequency / Hz") >>> plt.legend(["signal", "augmented signal"]) >>> plt.grid(alpha=0.4) >>> sns.despine() >>> plt.tight_layout()
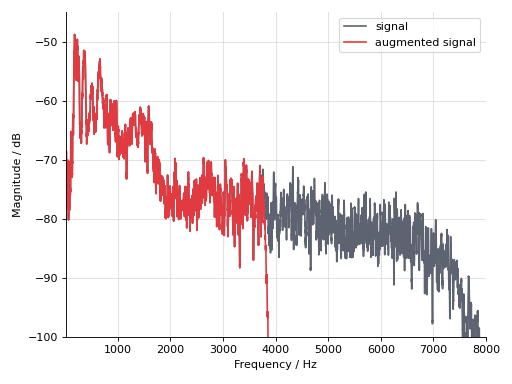
Removing the upper half of the signal by frst resampling it to 8000 Hz, and then to 32000 Hz. Again, we listen to the augmented signal at its original sampling rate of 16000 Hz.
>>> transform = auglib.transform.Compose( ... [ ... auglib.transform.Resample(8000), ... auglib.transform.Resample(32000), ... ], ... ) >>> augmented_signal = transform(signal, sampling_rate) >>> audplot.waveform(augmented_signal)

Inspect its magnitude spectrum.
>>> sigs = [signal, augmented_signal] >>> for sig, color in zip(sigs, colors): ... magnitude, f = plt.mlab.magnitude_spectrum(sig, Fs=sampling_rate) ... # Smooth magnitude ... magnitude = np.convolve(magnitude, np.ones(14) / 14, mode="same") ... plt.plot(f, audmath.db(magnitude), color=color) >>> plt.xlim([10, 8000]) >>> plt.ylim([-100, -45]) >>> plt.ylabel("Magnitude / dB") >>> plt.xlabel("Frequency / Hz") >>> plt.legend(["signal", "augmented signal"]) >>> plt.grid(alpha=0.4) >>> sns.despine() >>> plt.tight_layout()
__call__()¶
- Resample.__call__(signal, sampling_rate=None)¶
Apply transform to signal.
- Parameters
signal (
numpy.ndarray) – signal to be transformedsampling_rate (
typing.Optional[int]) – sampling rate in Hz
- Return type
- Returns
augmented signal
- Raises
ValueError – if the signal shape is not support by chosen transform parameters
ValueError – if
sampling_rateisNone, but the transform requires a samling rateRuntimeError – if the given sampling rate is incompatible with the transform
arguments¶
- Resample.arguments¶
Returns arguments that are serialized.
- Returns
Dictionary of arguments and their values.
- Raises
RuntimeError – if arguments are found that are not assigned to attributes of the same name
Examples
>>> import audobject.testing >>> o = audobject.testing.TestObject('test', point=(1, 1)) >>> o.arguments {'name': 'test', 'point': (1, 1)}
borrowed_arguments¶
- Resample.borrowed_arguments¶
Returns borrowed arguments.
- Returns
Dictionary with borrowed arguments.
id¶
- Resample.id¶
Object identifier.
The ID of an object ID is created from its non-hidden arguments.
- Returns
object identifier
Examples
>>> class Foo(Object): ... def __init__(self, bar: str): ... self.bar = bar >>> foo1 = Foo('I am unique!') >>> foo1.id '893df240-babe-d796-cdf1-c436171b7a96' >>> foo2 = Foo('I am different!') >>> foo2.id '9303f2a5-bfc9-e5ff-0ffa-a9846e2d2190' >>> foo3 = Foo('I am unique!') >>> foo1.id == foo3.id True
is_loaded_from_dict¶
- Resample.is_loaded_from_dict¶
Check if object was loaded from a dictionary.
Returns
Trueif object was initialized from a dictionary, e.g. after loading it from a YAML file.- Returns
Trueif object was loaded from a dictionary,otherwise
False
short_id¶
- Resample.short_id¶
Short object identifier.
The short ID consists of eight characters and is created from its non-hidden arguments.
- Returns
short object identifier
Examples
>>> class Foo(Object): ... def __init__(self, bar: str): ... self.bar = bar >>> foo1 = Foo('I am unique!') >>> foo1.id '893df240-babe-d796-cdf1-c436171b7a96' >>> foo1.short_id '171b7a96' >>> foo2 = Foo('I am different!') >>> foo2.short_id '6e2d2190' >>> foo3 = Foo('I am unique!') >>> foo1.short_id == foo3.short_id True
to_dict()¶
- Resample.to_dict(*, include_version=True, flatten=False, root=None)¶
Converts object to a dictionary.
Includes items from
audobject.Object.arguments. If an argument has a resolver, its value is encoded. Usually, the object can be re-instantiated usingaudobject.Object.from_dict(). However, ifflatten=True, this is not possible.- Parameters
include_version (
bool) – add version to class nameflatten (
bool) – flatten the dictionaryroot (
typing.Optional[str]) – if file is written to disk, set to target directory
- Return type
typing.Dict[str,typing.Union[bool,datetime.datetime,dict,float,int,list,None,str]]- Returns
dictionary that represent the object
Examples
>>> import audobject.testing >>> o = audobject.testing.TestObject('test', point=(1, 1)) >>> o.to_dict(include_version=False) {'$audobject.core.testing.TestObject': {'name': 'test', 'point': [1, 1]}} >>> o.to_dict(flatten=True) {'name': 'test', 'point.0': 1, 'point.1': 1}
to_samples()¶
to_yaml()¶
- Resample.to_yaml(path_or_stream, *, include_version=True)¶
Save object to YAML file.
- Parameters
path_or_stream (
typing.Union[str,typing.IO]) – file path or streaminclude_version (
bool) – add version to class name