CompressDynamicRange¶
- class auglib.transform.CompressDynamicRange(threshold_db, ratio, *, attack_time=0.01, release_time=0.02, knee_radius_db=4.0, makeup_db=0.0, clip=False, preserve_level=False, bypass_prob=None)[source]¶
Compress the dynamic range.
The dynamic range of the signal is compressed by attenuating any sample whose amplitude exceeds a certain
threshold_db. The intensity of the attenuation is determined by theratioparameter (the higher the ratio, the stronger the gain reduction). To avoid heavy distortion, the gain reduction is smoothed over time with a contour that is governed by theattack_timeand therelease_timeparameters.The input-output characteristic also features a non-linear region (“knee”) around the threshold. The width of this region is controlled by the
knee_radius_dbparameter (expressed in decibels, and in absolute value): the nonlinear region is entered when the input signal exceeds a level given bythreshold_db - kneeRadius_db, hence some gain reduction can be also seen before hitting the main threshold, if the knee radius is greater than zero.Optionally, the resulting signal can be amplified (linearly) by means of the
makeup_dbgain parameter (expressed in decibels). Sample values can also be clipped to the interval[-1.0, 1.0]when exceeding this range: this behaviour is achieved by setting theclipargument.Note
Setting
makeup_dbtoNonetriggers a special behaviour, for which the makeup gain is computed automatically in a way that the peak level of the processed signal is equal to the original peak level (before compression).- Parameters
threshold_db (
typing.Union[float,auglib.core.observe.Base]) – threshold in decibelsratio (
typing.Union[float,auglib.core.observe.Base]) – ratio (the higher the ratio, the stronger the gain reduction)attack_time (
typing.Union[float,auglib.core.observe.Base]) – attack time in secondsrelease_time (
typing.Union[float,auglib.core.observe.Base]) – release time in secondsmakeup_db (
typing.Union[None,float,auglib.core.observe.Base]) – optional amplification gainclip (
typing.Union[bool,auglib.core.observe.Base]) – clip signalpreserve_level (
typing.Union[bool,auglib.core.observe.Base]) – ifTruethe root mean square value of the augmented signal will be the same as before augmentationbypass_prob (
typing.Union[float,auglib.core.observe.Base,None]) – probability to bypass the transformation
Examples
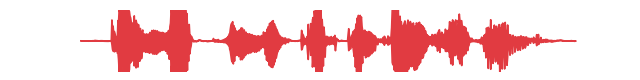
Attenuate all samples of a speech signal above -15 dB by a factor of 4.
>>> import audb >>> import audiofile >>> import audplot >>> import auglib >>> transform = auglib.transform.CompressDynamicRange(-15, 1 / 4) >>> files = audb.load_media("emodb", "wav/03a01Fa.wav", version="1.4.1") >>> signal, sampling_rate = audiofile.read(files[0]) >>> augmented_signal = transform(signal, sampling_rate) >>> audplot.waveform(augmented_signal)
__call__()¶
- CompressDynamicRange.__call__(signal, sampling_rate=None)¶
Apply transform to signal.
- Parameters
signal (
numpy.ndarray) – signal to be transformedsampling_rate (
typing.Optional[int]) – sampling rate in Hz
- Return type
- Returns
augmented signal
- Raises
ValueError – if the signal shape is not support by chosen transform parameters
ValueError – if
sampling_rateisNone, but the transform requires a samling rateRuntimeError – if the given sampling rate is incompatible with the transform
arguments¶
- CompressDynamicRange.arguments¶
Returns arguments that are serialized.
- Returns
Dictionary of arguments and their values.
- Raises
RuntimeError – if arguments are found that are not assigned to attributes of the same name
Examples
>>> import audobject.testing >>> o = audobject.testing.TestObject('test', point=(1, 1)) >>> o.arguments {'name': 'test', 'point': (1, 1)}
borrowed_arguments¶
- CompressDynamicRange.borrowed_arguments¶
Returns borrowed arguments.
- Returns
Dictionary with borrowed arguments.
id¶
- CompressDynamicRange.id¶
Object identifier.
The ID of an object ID is created from its non-hidden arguments.
- Returns
object identifier
Examples
>>> class Foo(Object): ... def __init__(self, bar: str): ... self.bar = bar >>> foo1 = Foo('I am unique!') >>> foo1.id '893df240-babe-d796-cdf1-c436171b7a96' >>> foo2 = Foo('I am different!') >>> foo2.id '9303f2a5-bfc9-e5ff-0ffa-a9846e2d2190' >>> foo3 = Foo('I am unique!') >>> foo1.id == foo3.id True
is_loaded_from_dict¶
- CompressDynamicRange.is_loaded_from_dict¶
Check if object was loaded from a dictionary.
Returns
Trueif object was initialized from a dictionary, e.g. after loading it from a YAML file.- Returns
Trueif object was loaded from a dictionary,otherwise
False
short_id¶
- CompressDynamicRange.short_id¶
Short object identifier.
The short ID consists of eight characters and is created from its non-hidden arguments.
- Returns
short object identifier
Examples
>>> class Foo(Object): ... def __init__(self, bar: str): ... self.bar = bar >>> foo1 = Foo('I am unique!') >>> foo1.id '893df240-babe-d796-cdf1-c436171b7a96' >>> foo1.short_id '171b7a96' >>> foo2 = Foo('I am different!') >>> foo2.short_id '6e2d2190' >>> foo3 = Foo('I am unique!') >>> foo1.short_id == foo3.short_id True
to_dict()¶
- CompressDynamicRange.to_dict(*, include_version=True, flatten=False, root=None)¶
Converts object to a dictionary.
Includes items from
audobject.Object.arguments. If an argument has a resolver, its value is encoded. Usually, the object can be re-instantiated usingaudobject.Object.from_dict(). However, ifflatten=True, this is not possible.- Parameters
include_version (
bool) – add version to class nameflatten (
bool) – flatten the dictionaryroot (
typing.Optional[str]) – if file is written to disk, set to target directory
- Return type
typing.Dict[str,typing.Union[bool,datetime.datetime,dict,float,int,list,None,str]]- Returns
dictionary that represent the object
Examples
>>> import audobject.testing >>> o = audobject.testing.TestObject('test', point=(1, 1)) >>> o.to_dict(include_version=False) {'$audobject.core.testing.TestObject': {'name': 'test', 'point': [1, 1]}} >>> o.to_dict(flatten=True) {'name': 'test', 'point.0': 1, 'point.1': 1}
to_samples()¶
to_yaml()¶
- CompressDynamicRange.to_yaml(path_or_stream, *, include_version=True)¶
Save object to YAML file.
- Parameters
path_or_stream (
typing.Union[str,typing.IO]) – file path or streaminclude_version (
bool) – add version to class name
to_yaml_s()¶
- CompressDynamicRange.to_yaml_s(*, include_version=True)¶
Convert object to YAML string.
Examples
>>> import audobject.testing >>> o = audobject.testing.TestObject('test', point=(1, 1)) >>> print(o.to_yaml_s(include_version=False)) $audobject.core.testing.TestObject: name: test point: - 1 - 1