Append¶
- class auglib.transform.Append(aux, *, read_pos_aux=0.0, read_dur_aux=None, unit='seconds', transform=None, preserve_level=False, bypass_prob=None)[source]¶
Append an auxiliary signal.
- Parameters
aux (
typing.Union[str,auglib.core.observe.Base,numpy.ndarray,auglib.core.transform.Base]) – auxiliary signal, file, or signal generating transform. If a transform is given it will be applied to an empty signal with the same shape as the signal the transform is applied toread_pos_aux (
typing.Union[int,float,auglib.core.observe.Base,auglib.core.time.Time]) – read position of auxiliary signal (seeunit)read_dur_aux (
typing.Union[int,float,auglib.core.observe.Base,auglib.core.time.Time,None]) – duration to read from auxiliary signal (seeunit). Set toNoneor0to read the whole signalunit (
str) – literal specifying the format ofread_pos_auxandread_dur_aux(seeauglib.utils.to_samples())transform (
typing.Optional[auglib.core.transform.Base]) – transformation applied to the auxiliary signalpreserve_level (
typing.Union[bool,auglib.core.observe.Base]) – ifTruethe root mean square value of the augmented signal will be the same as before augmentationbypass_prob (
typing.Union[float,auglib.core.observe.Base,None]) – probability to bypass the transformation
Examples
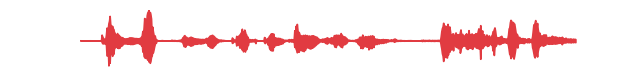
Append coughing at the end of a speech signal.
>>> import audb >>> import audiofile >>> import audplot >>> import auglib >>> files = audb.load_media( ... "cough-speech-sneeze", ... "coughing/kopzxumj430_40.94-41.8.wav", ... version="2.0.1", ... sampling_rate=16000, ... ) >>> cough, _ = audiofile.read(files[0]) >>> transform = auglib.transform.Append(cough) >>> files = audb.load_media("emodb", "wav/03a01Fa.wav", version="1.4.1") >>> signal, _ = audiofile.read(files[0]) >>> augmented_signal = transform(signal) >>> audplot.waveform(augmented_signal)
__call__()¶
- Append.__call__(signal, sampling_rate=None)¶
Apply transform to signal.
- Parameters
signal (
numpy.ndarray) – signal to be transformedsampling_rate (
typing.Optional[int]) – sampling rate in Hz
- Return type
- Returns
augmented signal
- Raises
ValueError – if the signal shape is not support by chosen transform parameters
ValueError – if
sampling_rateisNone, but the transform requires a samling rateRuntimeError – if the given sampling rate is incompatible with the transform
arguments¶
- Append.arguments¶
Returns arguments that are serialized.
- Returns
Dictionary of arguments and their values.
- Raises
RuntimeError – if arguments are found that are not assigned to attributes of the same name
Examples
>>> import audobject.testing >>> o = audobject.testing.TestObject('test', point=(1, 1)) >>> o.arguments {'name': 'test', 'point': (1, 1)}
borrowed_arguments¶
- Append.borrowed_arguments¶
Returns borrowed arguments.
- Returns
Dictionary with borrowed arguments.
id¶
- Append.id¶
Object identifier.
The ID of an object ID is created from its non-hidden arguments.
- Returns
object identifier
Examples
>>> class Foo(Object): ... def __init__(self, bar: str): ... self.bar = bar >>> foo1 = Foo('I am unique!') >>> foo1.id '893df240-babe-d796-cdf1-c436171b7a96' >>> foo2 = Foo('I am different!') >>> foo2.id '9303f2a5-bfc9-e5ff-0ffa-a9846e2d2190' >>> foo3 = Foo('I am unique!') >>> foo1.id == foo3.id True
is_loaded_from_dict¶
- Append.is_loaded_from_dict¶
Check if object was loaded from a dictionary.
Returns
Trueif object was initialized from a dictionary, e.g. after loading it from a YAML file.- Returns
Trueif object was loaded from a dictionary,otherwise
False
short_id¶
- Append.short_id¶
Short object identifier.
The short ID consists of eight characters and is created from its non-hidden arguments.
- Returns
short object identifier
Examples
>>> class Foo(Object): ... def __init__(self, bar: str): ... self.bar = bar >>> foo1 = Foo('I am unique!') >>> foo1.id '893df240-babe-d796-cdf1-c436171b7a96' >>> foo1.short_id '171b7a96' >>> foo2 = Foo('I am different!') >>> foo2.short_id '6e2d2190' >>> foo3 = Foo('I am unique!') >>> foo1.short_id == foo3.short_id True
to_dict()¶
- Append.to_dict(*, include_version=True, flatten=False, root=None)¶
Converts object to a dictionary.
Includes items from
audobject.Object.arguments. If an argument has a resolver, its value is encoded. Usually, the object can be re-instantiated usingaudobject.Object.from_dict(). However, ifflatten=True, this is not possible.- Parameters
include_version (
bool) – add version to class nameflatten (
bool) – flatten the dictionaryroot (
typing.Optional[str]) – if file is written to disk, set to target directory
- Return type
typing.Dict[str,typing.Union[bool,datetime.datetime,dict,float,int,list,None,str]]- Returns
dictionary that represent the object
Examples
>>> import audobject.testing >>> o = audobject.testing.TestObject('test', point=(1, 1)) >>> o.to_dict(include_version=False) {'$audobject.core.testing.TestObject': {'name': 'test', 'point': [1, 1]}} >>> o.to_dict(flatten=True) {'name': 'test', 'point.0': 1, 'point.1': 1}
to_samples()¶
to_yaml()¶
- Append.to_yaml(path_or_stream, *, include_version=True)¶
Save object to YAML file.
- Parameters
path_or_stream (
typing.Union[str,typing.IO]) – file path or streaminclude_version (
bool) – add version to class name